Assessment of Efficacy and Safety of Tislelizumab for Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.70844/jmhrp.2025.2.2.43Keywords:
Tislelizumab, Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, Malignancies, Cancer, Efficacy, Safety, Tolerability, Cost analysisAbstract
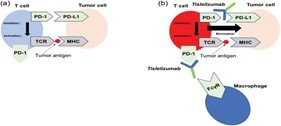
Background: Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma (ESCC) is a highly aggressive tumor with limited treatment options and poor global survival rates. The advent of immune checkpoint inhibitors has reshaped therapeutic strategies, with tislelizumab, a humanized PD-1 inhibitor engineered to minimize Fcγ receptor binding, emerging as a promising agent.
Methods: A literature search was performed using PubMed, Embase, Web of Science and ClinicalTrials.gov up to September 2025. Peer-reviewed articles, randomized controlled trials, prospective and retrospective cohort studies, pooled safety analyses, pharmacokinetic reports and real-world studies reporting on tislelizumab in ESCC were included. Abstracts from major oncology congresses (ASCO, ESMO, CSCO) were also reviewed. Evidence was systematically extracted and synthesized to evaluate pharmacologic properties, efficacy outcomes, safety and tolerability, patient-reported outcomes, as well as ongoing investigational trials. Economic analyses and cost-effectiveness reports were screened but summarized separately.
Results: In the second-line setting, tislelizumab monotherapy has demonstrated superior overall survival and a more favorable safety profile compared with chemotherapy, establishing it as a validated treatment option. In the first-line setting, the addition of tislelizumab to platinum–fluoropyrimidine chemotherapy significantly improves overall survival, progression-free survival and objective response rates, with benefits observed across most subgroups. Patient-reported outcomes indicate slower deterioration in global health status and physical functioning compared with chemotherapy alone. Preliminary studies in the neoadjuvant and perioperative settings show promising pathological responses, although long-term survival data are still awaited. Pharmacokinetic and exposure–response analyses support a fixed 200 mg intravenous dose every three weeks, with low immunogenicity and no routine need for dose adjustments in patients with mild-to-moderate hepatic or renal impairment. Safety analyses confirm that tislelizumab is generally well tolerated, with immune-related adverse events manageable through established treatment algorithms.
Conclusion: Tislelizumab has established itself as an effective and tolerable treatment for ESCC, improving both survival outcomes and quality of life of patients. While uncertainties remain regarding biomarker refinement, optimal sequencing and cost-effectiveness outside of China, the current evidence supports tislelizumab as a key component of the evolving treatment paradigm for ESCC underscoring the need for further trials to expand its role in earlier disease stages and broader patient populations. Additionally. generalizability outside Asia remains uncertain due to differences in drug pricing, healthcare access and limited head-to-head data against other PD-1 inhibitors.